Nucleic Acid Isar valley begins work
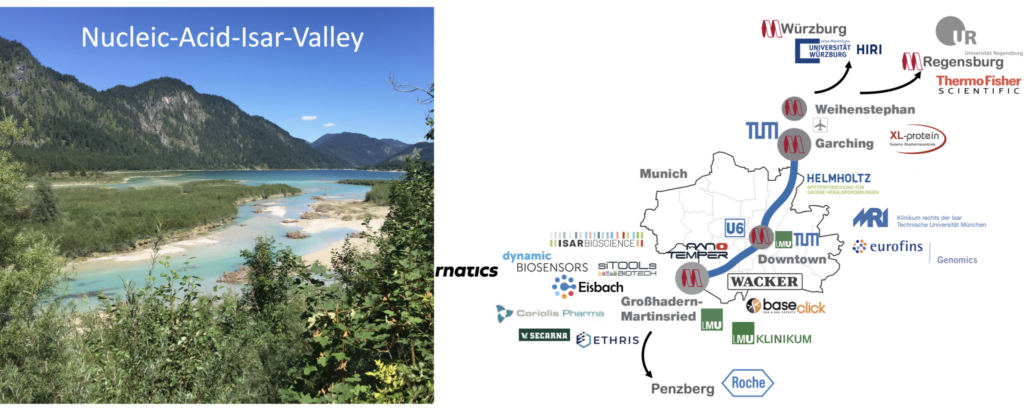
Am 1. Mai 2023 hat unser Zukunftscluster für Nukleinsäure-Therapeutika CNATM seine Arbeit aufgenommen. CNATM besteht aus Wissenschaftlern und Wissenschaftlerinnen der federführenden Universitäten der LMU und der TUM, unter Beteiligung der Universitäten von Regensburg und Würzburg, dem Helmholtz-Zentrum München und 14 Unternehmen aus der Region im Großraum München.